Remember that enzymes usually end in ase; catalase, sucrase.
The enormous of biochemical reactions occurring within cells is
regulated by enzymes. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions, as well as
control the rate at which reactions occur. They are globular protein
molecules manufactured by each cell. More than 2000 enzymes have been
recognized based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. All of them
are structurally different.
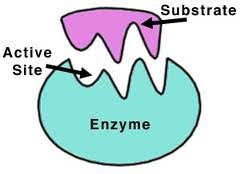
An enzyme recognizes a specific molecule called a substrate and binds to
it. Some enzymes are so specific they only act on one substrate, while
others can act on a class of substrate.
Enzymes can bring about changes to molecule to which it binds. The
change usually involves the forming or breaking of a covalent chemical
bond. Enzymes may split the substrate into two pieces, may add a
chemical side group to the molecule, or may simply rearrange the bonds
in the substrate.

Enzymes lower the activation energy by 1) providing a medium that is
more favorable than the surrounding one. 2) By bringing the reactant
into close contact. 3) They might add or remove a proton from the
substrate , strain the substrate molecule's bond, or even form temporary
covalent bond between the substrate and some part of the enzyme itself.








 Bacterium
Bacterium The Ameoba
The Ameoba