Have a great holiday and all the best for the new decade.
See you all in 2020
See you all in 2020
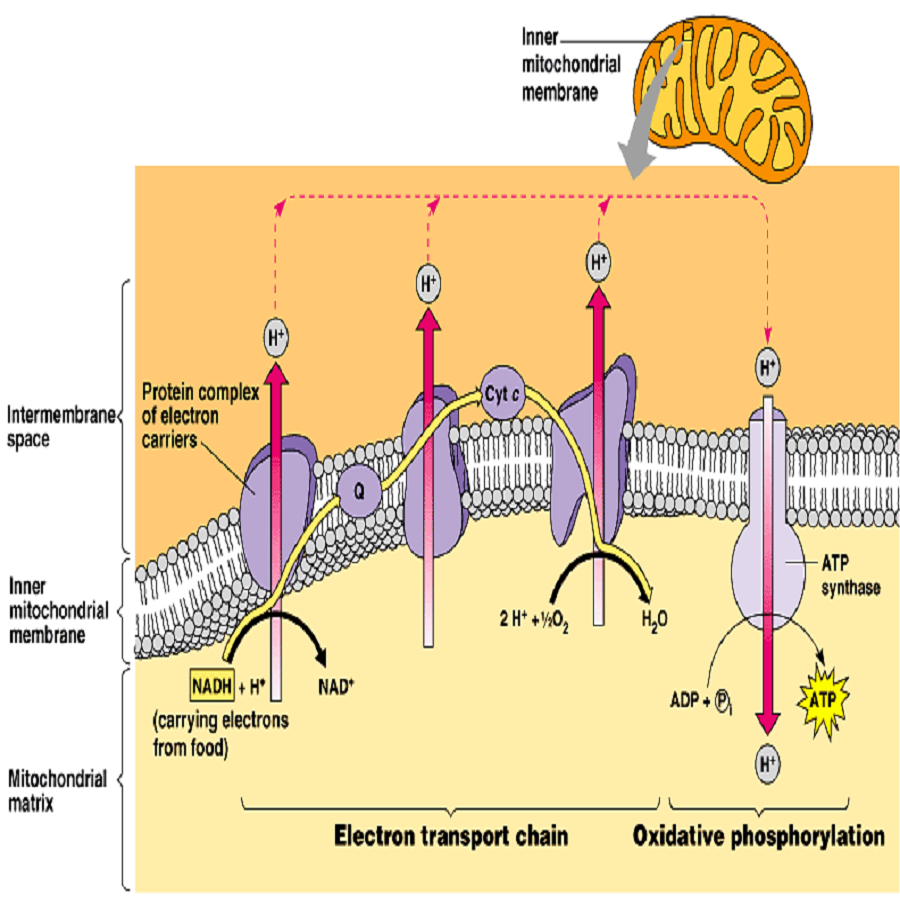
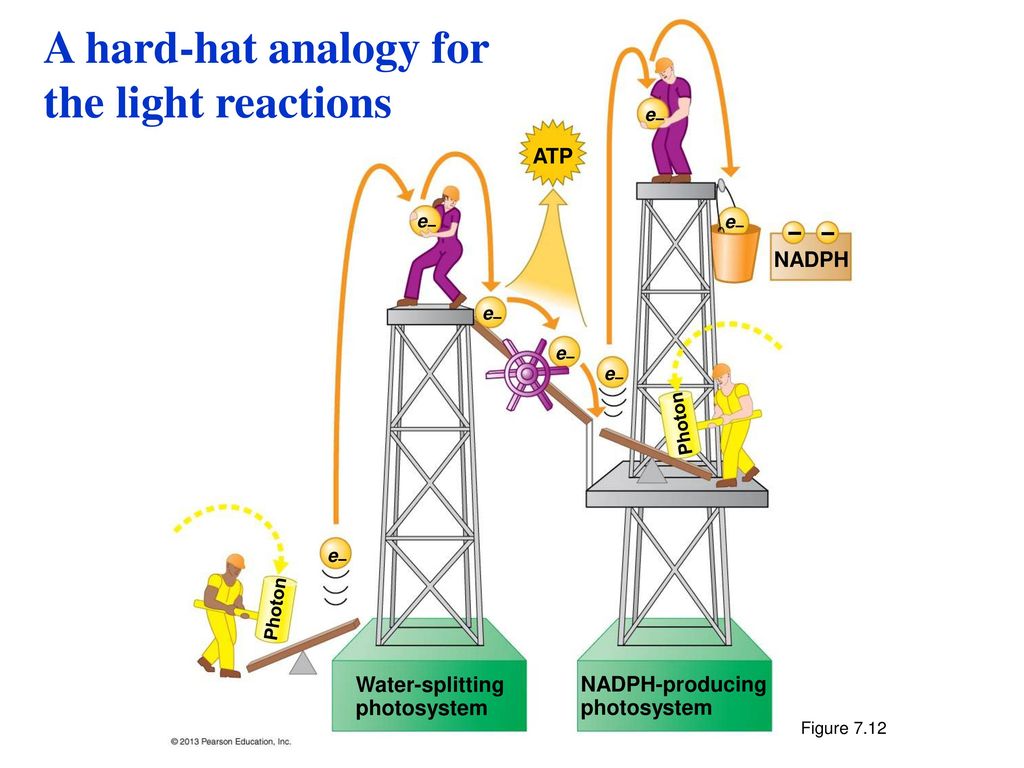 Image from Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology. 4th Edition.
Image from Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology. 4th Edition.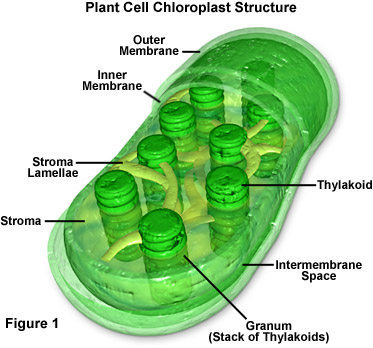







 ....
....


MEMBRANE SEPARATES TWO SOLUTIONS WITH DIFFERENT SUGAR CONCENTRATIONS. WATER MOLECULES CAN PASS THROUGH THE MEMBRANE, BUT SUGAR MOLECULES CANNOT.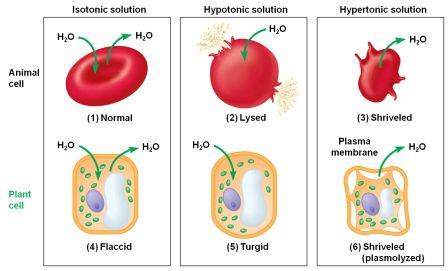 CLICK ON THE LINKS BELOW TO VIEW REAL LIFE EXAMPLE OF WATER RUSHING INTO THE CELLS, THUS CAUSING WATER POISONING.
Court Settlement for the Water Poisoning Death
WATER INTOXICATION, ALSO KNOWN AS WATER POISONING, OVERHYDRATION, OR WATER TOXEMIA IS A POTENTIALLY FATAL DISTURBANCE IN BRAIN FUNCTIONS THAT RESULTS WHEN THE NORMAL BALANCE OF ELECTROLYTES IN THE BODY IS PUSHED OUTSIDE SAFE LIMITS BY EXCESSIVE WATER INTAKE.Endurance sportsMarathon runners are susceptible to water intoxication if they drink too much while running. This is caused when sodium levels drop below 135 μmol/L when athletes consume large amounts of fluid. This has been noted to be the result of the encouragement of excessive fluid replacement by various guidelines. This has largely been identified in marathon runners as a dilutional hyponatremia.[5] A study conducted on participants of the 2002 Boston Marathon found that thirteen percent finished the race with hyponatremia. The study concluded that the strongest predictor of hyponatremia ( low sodium levels in the blood) was weight gain while racing (over-hydration), and hyponatremia was just as likely to occur in runners who chose sports drinks as those who chose water.[5] Medical personnel at marathon events are trained to suspect water intoxication immediately when runners collapse or show signs of confusion.The information above explaining water intoxication was copied from Wikipedia |




 Bacterium
Bacterium The Ameoba
The Ameoba