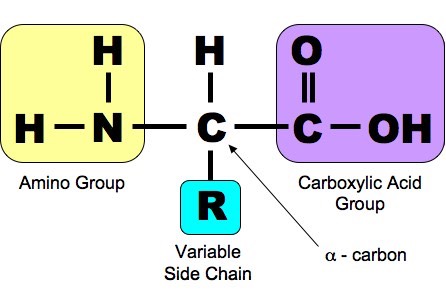
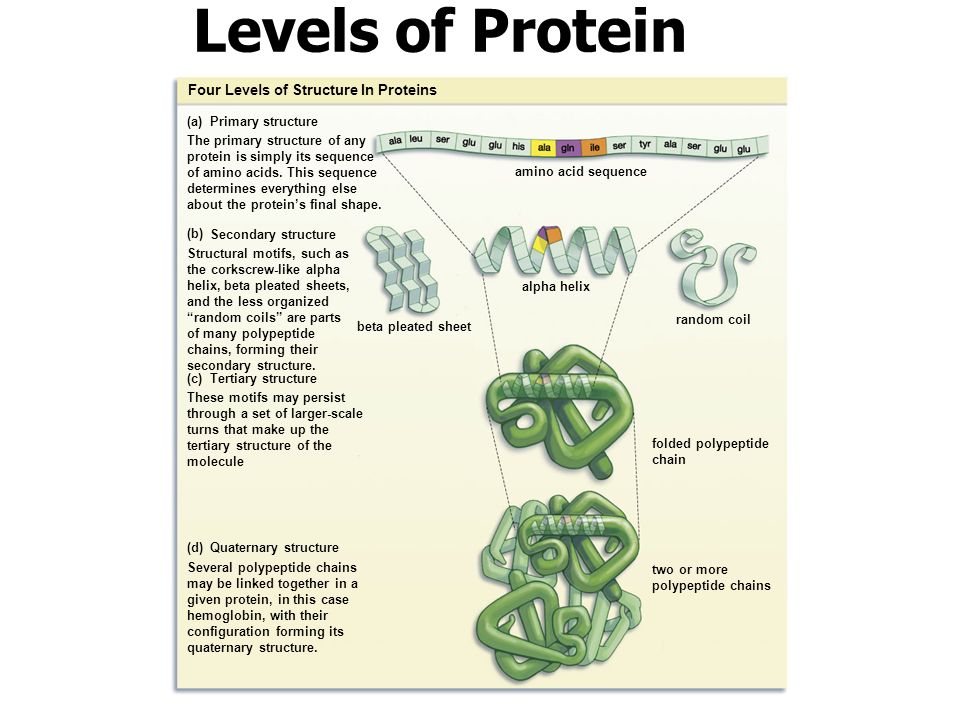
Protein is a polymer of amino acid monomers. Proteins are the most elaborate and diverse of life's molecules. Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry weight of most cells, and they are instrumental in almost everything.
It is only in the nature of the variant (R) that amino acids differ from
one another. There are only about twenty amino acids that occur in the
proteins of living organisms, although there are more than 2000 natural
and artificially made amino acids.
There are ten essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be included in the diet.

Nucleic Acids
You will be introduced to nucleic acids. The details of nucleic acids
will be covered later in the school year under the units on genetics.
The monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made
of a phosphate group, linked to a 5-carbon sugar. Each nucleic acid
chain has a backbone in which phosphate groups alternate with sugar
molecules to form a covalently linked polymer. Attached to the sugar
ring of each nucleotide by loss of a molecule is one of four nitrogenous
bases: A, T, C and G.
If the proteins are the building materials of life, then nucleic acids
are the blueprint. The DNA has the instructions and directs the RNA in
functioning of cells and the synthesis of proteins
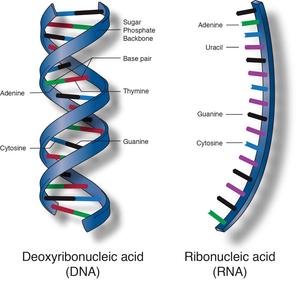



 The DNA Molecule
The DNA Molecule